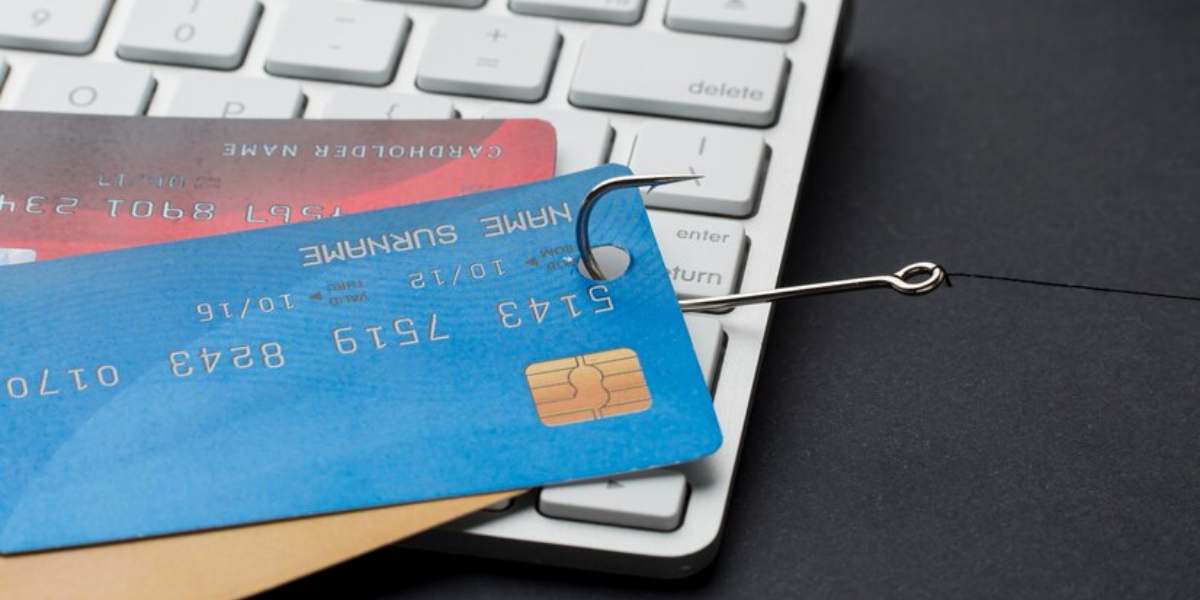
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a technique that cybercriminals use to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and other sensitive data or to install malware on your device. The goal is to trick the victim through fraudulent means such as fake emails and websites that appear to be from legitimate sources. Phishing attacks can be quite advanced and sophisticated, using realistic-looking logos, email addresses, and even personal information to deceive the victim.
Unfortunately, the consequences of falling victim to a phishing attack are severe and result in issues such as identity theft, financial losses, and major security breaches. As such, it is important to be cautious and vigilant whenever sharing personal information online. Here’s an overview of traces cybercriminals leave behind:
Email Breakdown: Warning Signs of Phishing
From Sender Line
- You don’t recognize the sender’s email address
- The sender is supposedly from a known contact, but the message is unusual or out of character
- The sender’s email address has a suspicious domain. (ex. apple-support.com)
To Recipient Line
- You were cc’d with other people you don’t know
- Other cc’d people’s last name all starts with the same letter
- The mix of cc’d addresses seem unrelated
Date and Time
- The email was sent at an unusual time outside of normal business hours (ex. 2 a.m.)
Subject
- The subject is presented as a reply or in reference to something you never requested
Thoroughly look for signs of phishing before interacting with emails.
Attachments
- The attachment makes no sense in relation to the email
- The sender doesn’t normally send you this kind of attachment or you weren’t expecting it
Content
- The email conveys extreme urgency
- There’s grammar and spelling mistakes
- What the sender is asking you to do seems odd or doesn’t make sense
- The sender is telling you you’ll gain something or avoid something negative if you click on a link
Hyperlinks
- When you hover your mouse over a hyperlink, the link-to address is different from what is displayed
- The hyperlink is slightly off (ex. www.Qua1ityd0s.com instead of www.qualitydos.com)
- There is nothing else in the email’s body except for the hyperlink
How to Protect Yourself from Phishing
Being aware of the warning signs of phishing scams and educating your employees on them is a critical step in safeguarding your business from becoming a victim. However, there are other steps you can take to protect yourself from this type of cyberattack as well. Installing security software on your computer and regularly keeping it updated will help deter security threats. Using multi-factor authentication and backing up your data to an external hard drive or in the cloud are also smart measures.
In the event you have responded to a phishing email, the Federal Trade Commision has advice on what you should do:
“If you think a scammer has your information, like your Social Security, credit card, or bank account number, go to IdentityTheft.gov. There, you’ll see the specific steps to take based on the information that you lost. If you think you clicked on a link or opened an attachment that downloaded harmful software, update your computer’s security software. Then run a scan and remove anything it identifies as a problem.”
Following these proactive steps and staying informed about potential phishing dangers will help you significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to such attacks. Thus, you’ll be able to better protect your personal and business information. Want to learn more information about how to boost your cybersecurity? Check out our blog on how to keep data secure with managed print services. Remember, cybersecurity is everyone's responsibility. Stay vigilant and help create a safer digital landscape.




